The future of work is rapidly changing, and so should your Learning and Development (L&D) strategy. Discover 10 cutting-edge trends that will help your workforce stay ahead of the curve and thrive in the years to come.
The landscape of work is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Automation, artificial intelligence, and the ever-evolving digital landscape are redefining the skills and knowledge needed to succeed. In this dynamic environment, traditional Learning and Development (L&D) approaches may no longer suffice. To empower your workforce and ensure their continued success, it’s crucial to embrace innovative L&D trends that are tailored to the future of work.
|
Author: Jonathan M. Pham |
Highlights
- This article explores 10 transformative trends that are reshaping the future of Learning and Development (L&D). It emphasizes the critical role of continuous learning and adaptability for organizations to stay competitive.
- The focus shifts to equipping the workforce with future-proof skills through upskilling and reskilling, while acknowledging the growing importance of soft skills alongside technical expertise.
- The article also delves into innovative approaches like Generative AI, immersive learning, and mobile/social learning, highlighting the importance of data-driven measurement to assess the impact of L&D initiatives.
- Finally, it underscores the need for L&D to prioritize Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DE&I) to create a thriving and resilient workforce.

The Rise of Continuous Learning and Organizational Agility
The business landscape is more dynamic than ever. New technologies, evolving customer needs, and ever-shifting competition demand organizations to be adaptable and responsive. This has led to a surge in the trend of organizational agility and continuous learning.
What it means:
- Organizational Agility: The ability of an organization to quickly identify, adapt to, and even thrive in the face of change. It involves flexible structures, empowered employees, and a willingness to experiment and learn from failures.
- Continuous Learning: A culture where team members are encouraged and supported in acquiring new skills and knowledge throughout their careers. This ensures the workforce stays relevant and adaptable to evolving needs.
How organizations can prepare:
- Shifting L&D Focus: Move away from one-size-fits-all training programs and design adaptable learning experiences. This could involve microlearning modules, on-demand resources, and peer-to-peer knowledge sharing.
- Building a Learning Culture: Foster a growth mindset where experimentation and learning from mistakes are encouraged. Leaders may set the tone by actively participating in learning initiatives and demonstrating a willingness to adapt.
- Investing in Technology: Utilize Learning Management Systems (LMS) and other digital tools to deliver personalized learning pathways, track progress, and encourage collaboration.
- Encouraging Knowledge Sharing: Create platforms and opportunities for individuals to share their expertise with each other. This could involve internal knowledge repositories, mentorship programs, or brown bag lunch sessions.
Examples:
- A marketing team facing a new social media platform might utilize microlearning modules to quickly equip themselves with the necessary skills to launch successful campaigns.
- A financial services company implements a knowledge-sharing platform where people are able to post questions and receive answers from colleagues across different departments, fostering cross-functional learning.

Read more: Agility Coaching – Navigating Change & Fueling Business Success
Upskilling and Reskilling: Keeping Your Workforce Future-Proof
In the face of a rapidly changing technological landscape, organizations are increasingly focusing on developing their workforce – so that team members are equipped with the necessary skill sets to remain relevant and productive in their roles.
- Upskilling: Equipping employees with new skills and knowledge that enhance their current job functions – whether through learning new software, developing stronger communication skills, or deepening their understanding of industry trends.
- Reskilling: Providing them with the competencies they need to transition into entirely new job roles within the organization. This is often necessary when technology disrupts existing roles or new business needs emerge.
Why it’s important:
- Keeps pace with updates: New technologies are constantly emerging; as such, upskilling ensures your workforce can leverage these advancements for improved efficiency and productivity.
- Adapts to changing business needs: As business strategies evolve, reskilling allows you to redeploy talent to meet new requirements.
- Boosts employee morale: Investing in people’s development demonstrates your commitment to their growth and fosters a sense of job security.
How organizations can prepare:
- Skills Gap Analysis: Conduct a thorough assessment of your current workforce skills and compare them to future needs – whether through surveys, manager feedback, or analyzing industry trends. This will help identify areas for improvement and prioritize training programs.
- Personalized Learning Paths: Design customized learning paths for team members based on their individual strengths, weaknesses, and career aspirations.
- Microlearning Opportunities: Offer bite-sized learning modules that are easily accessible and can be completed during short windows of time – so as to cater to busy schedules and allow for on-the-go learning. Additionally, consider incorporating gamification techniques to further boost motivation and knowledge retention.
- Partnerships with Educational Institutions: Collaborate with universities, colleges, or online learning platforms to offer relevant training programs and certifications.
Read more: Training Needs Analysis (TNA) – From Insight to Impact

The Rise of Soft Skills
While technical skills are crucial for completing specific tasks, soft skills are the foundation for success in any role and working environment – and even more relevant in today’s dynamic business landscape.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: The modern workplace thrives on collaboration across teams and departments. Being able to actively listen and demonstrate empathy to others enables individuals to work effectively together toward a common goal.
- Problem-solving and Critical Thinking: Today’s work demands the ability to analyze situations, identify problems, and develop creative solutions. Critical thinking and problem-solving competencies help team members navigate complex challenges and adapt to changing circumstances.
- Communication: Clear and concise communication is essential for information sharing, decision-making, and building trust within teams. Skills like written and verbal communication ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Emotional Intelligence: The ability to understand and manage emotions, both yours and those of others, is crucial for navigating workplace dynamics and building strong relationships.
Heeding this trend, many organizations are implementing dedicated training programs to develop soft skills in their employees – especially those in management positions. These involve workshops on communication techniques, conflict resolution strategies, or active listening exercises. In addition, mentorship and coaching sessions are often held – so that team members may develop soft skills through personalized feedback and guidance from experienced colleagues.

Learning and Development future trends
Generative AI Revolutionizes Corporate Training
The emergence of Generative AI (AI that creates new content) is a transformative trend in corporate training. It promises to address the growing need for personalized, engaging, and efficient learning experiences for a diverse workforce.
- Personalized Learning: Generative AI can analyze data on individual learners (e.g., skills, experience, learning style) and create customized learning paths. As such, each team member may receive the most relevant and impactful training.
- Content Creation on Steroids: AI can automate the creation of training materials, such as quizzes, simulations, and interactive scenarios. This frees up time and resources for L&D professionals to focus on strategic planning and content curation.
- Microlearning on Demand: At the same time, AI is also capable of creating bite-sized learning modules that cater to busy schedules and shorter attention spans. In other words, employees now have the option to learn in short bursts throughout the workday, therefore improving knowledge retention.
Examples of Generative AI in Action:
- Scenario-Based Training: Imagine a sales training program where AI generates personalized sales simulations based on the individual’s product knowledge, customer segment, and sales goals. That should be a highly realistic and relevant learning experience!
- Adaptive Learning Platform: A learning platform powered by generative AI tailors the learning path for each employee based on their performance in quizzes or interactive exercises. This ensures learners may focus on areas where they need the most improvement.
Preparing for the Generative AI Revolution:
- Invest in the Right Tools: Research and choose an AI platform that aligns with your specific training needs and budget. Consider factors like ease of use, content creation capabilities, and data security.
- Develop a Human-AI Collaboration Strategy: AI is a powerful tool; that said, it shouldn’t replace human expertise. Integrate these tools with the experience of L&D professionals to ensure content quality, learning objectives alignment, and human connection during the learning process.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: AI technology is constantly evolving. As such, organizations should promote a culture of continuous learning within their L&D team – so that they may stay updated on the latest advancements and apply them to their corporate training strategies.
Read more: AI in Leadership – Bridging the Gap Between Adoption & Maturity

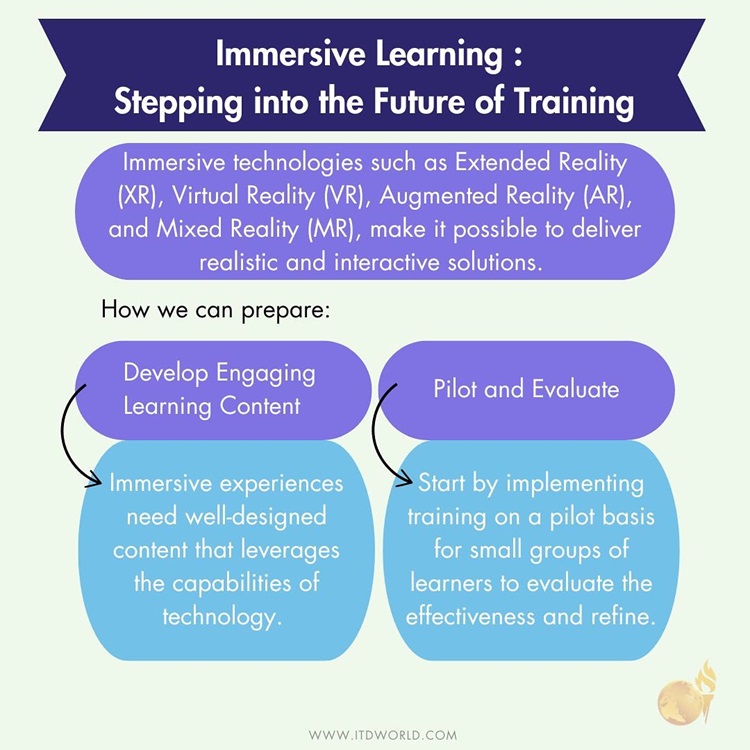
Immersive Learning: Stepping into the Future of Training
Immersive technologies, particularly those under the umbrella of Extended Reality (XR) – Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR) – make it possible to deliver highly realistic and interactive simulations. As such, learners are taken beyond traditional classroom settings and into the heart of the learning experience.
- Enhanced Engagement: Immersive environments capture learners’ attention and create a sense of presence, leading to deeper engagement with the training material.
- Safe Practice Environment: VR simulations allow participants to practice complex skills or procedures in a safe and controlled environment, without risk of real-world consequences.
- Improved Knowledge Retention: The interactive and hands-on nature of such learning experiences translates to better knowledge retention and recall compared to traditional methods.
Examples of Immersive Technologies in Action:
- VR Safety Training: Imagine a construction worker experiencing a VR simulation of a high-rise building site. They can practice identifying safety hazards, using equipment, and following safety protocols in a realistic virtual environment.
- AR Maintenance Training: A technician can wear AR glasses while performing maintenance on complex machinery. The glasses overlay digital instructions and schematics onto their real-world view, guiding them through the process step-by-step.
- MR Soft Skills Training: An employee may participate in a virtual meeting scenario using MR technology – where they are able to practice communication skills, conflict resolution techniques, and negotiation strategies with virtual avatars as colleagues.
How Organizations Can Prepare:
- Develop Engaging Learning Content: Immersive experiences require well-designed content that leverages the unique capabilities of each technology. Consider partnering with XR development companies to create high-quality, interactive learning modules.
- Pilot and Evaluate: Start by implementing immersive training on a pilot basis for a small group of learners. This allows you to evaluate its effectiveness and refine your approach before a wider rollout.
Mobile & Social Learning: A Powerful Combo
The convergence of mobile and social learning tools is a powerful trend expected to massively transform how employees learn and develop:
- Convenience and Flexibility: Mobile learning allows employees to access learning materials and complete training modules anytime, anywhere, on their smartphones or tablets; this caters to busy schedules and diverse learning styles.
- Microlearning on the Go: Mobile learning content is often delivered in bite-sized chunks, perfect for short bursts of learning throughout the workday.
- Offline Accessibility: Many apps allow users to download content for offline access. As a result, learning can continue even without an Internet connection.
- Collaborative Learning: Social learning platforms create opportunities for employees to connect, share knowledge, and learn from each other – which fosters a sense of community and encourages peer-to-peer learning.
- Gamification and Engagement: Social learning tools often incorporate gamification elements like badges, leaderboards, and points – which contribute to increasing engagement and motivation among learners.
- Real-time Knowledge Sharing: These platforms enable users to ask questions, share experiences, and get instant feedback from colleagues or experts. The result is a more dynamic learning environment.
How Organizations Can Prepare:
- Invest in Mobile-Friendly Learning Materials: Ensure your training content is optimized for mobile devices with clear visuals, concise text, and user-friendly navigation.
- Choose the Right Platform: Select a platform that caters to your specific needs and offers features like discussion forums, group collaboration tools, and knowledge-sharing functionalities.
- Develop a Strategy: Create a comprehensive strategy for mobile learning, including content creation, accessibility considerations, and employee onboarding for the new platform.

Learning and Development future trends
Strategic Alignment with Corporate Objectives
A major trend in L&D is the strategic alignment of training programs with the organization’s overall objectives. This ensures that employees are not just learning for the sake of learning, but developing the skills and knowledge needed to drive the company’s success.
Benefits:
- Improved ROI: By focusing on skills directly relevant to business goals, L&D investments demonstrate a clear return on investment (ROI) by contributing to improved performance and achieving strategic objectives.
- Increased Engagement: When team members see a clear connection between their learning and development and the company’s success, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated to participate in training programs.
- Future-Proofing the Workforce: By aligning L&D with evolving business needs, organizations may establish a workforce equipped with the competencies necessary to adapt to future challenges and opportunities.
Examples of Alignment in Action:
- Sales Training for New Market Entry: A company planning to enter a new market develops a sales training program tailored to the specific needs of that market. The training equips salespeople with the knowledge, communication skills, and cultural awareness necessary to be successful in the new territory.
- Leadership Development for Innovation: An organization aiming to foster a more innovative culture implements a leadership development program that emphasizes creative problem-solving, risk-taking, and collaboration.
- Customer Service Training for Improved Satisfaction: To address declining customer satisfaction scores, a company redesigns its customer service training program to address active listening, empathy, and conflict resolution skills – with the aim of improving customer interactions.
Read more: Future Ready Organization – 11 Tips to Building One Capable of Adapting to Industry Trends

Learning on the Fly: The Rise of Learning in the Flow of Work
The concept of “Learning in the Flow of Work” is gaining traction in L&D circles – specifically, learning opportunities are directly integrated into employees’ daily workflows, at the very moment they need the information. This approach aims to bridge the gap between theoretical training and practical application.
Benefits:
- Increased Relevance: Learning happens in context, directly addressing the task at hand. As a result, information is immediately applicable and contributes to reinforcing knowledge retention.
- Improved Productivity: As employees can access bite-sized learning modules quickly, the risk of work disruption is minimized. Not to mention, they may now learn and apply new skills while still completing their tasks.
- Enhanced Motivation: Learning feels less like a chore and more like a natural extension of work. This helps boost employee motivation and engagement with training materials.
Examples of Learning in the Flow of Work:
- Microlearning Modules: Short, targeted learning modules embedded within software applications or project management tools. For example, a content management system might offer pop-up tutorials on specific functionalities when a user encounters them.
- Contextual Help Overlays: Interactive overlays that appear within an application or program interface, providing step-by-step guidance for completing specific tasks. These overlays can be dynamically triggered based on user actions.
- Knowledge Management Platforms: Centralized repositories of searchable resources like knowledge base articles, FAQs, and video tutorials. Users can quickly access these resources to find answers and guidance while working on specific tasks.
Read more: Employee Engagement in the Digital Age – Strategies for Powering Up Your Workforce

Focus on Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DE&I)
Incorporating DE&I principles into training programs enables organizations to foster a more inclusive, respectful, and innovative work environment where individuals feel valued and empowered to contribute their unique talents.
Examples of DE&I in L&D Practices:
- Unconscious Bias Training: This type of training educates employees on implicit biases and how they can impact decision-making. It equips them with strategies to mitigate bias and promote fair treatment for everyone.
- Inclusive Learning Design: Training materials and courses/ workshops are designed to be accessible and inclusive for all learners, regardless of background, learning style, or ability. This might involve using diverse case studies, providing closed captions for videos, and offering content in multiple languages.
- Mentorship and Sponsorship Programs: Programs that connect underrepresented employees with experienced mentors or sponsors foster a sense of belonging and encourage diverse talent to thrive within the organization.
How Organizations Can Prepare:
- Conduct a DE&I Audit: Assess your current L&D programs to identify any potential biases or areas where inclusivity can be improved.
- Develop a DE&I L&D Strategy: Develop a comprehensive strategy that outlines how DE&I principles will be integrated into your training programs. This might involve setting specific goals, allocating resources, and identifying training partners with expertise in DE&I.
- Partner with Diverse Trainers and Experts: Engage facilitators and content creators with diverse backgrounds and experiences to ensure your training programs are inclusive and reflect a variety of perspectives.

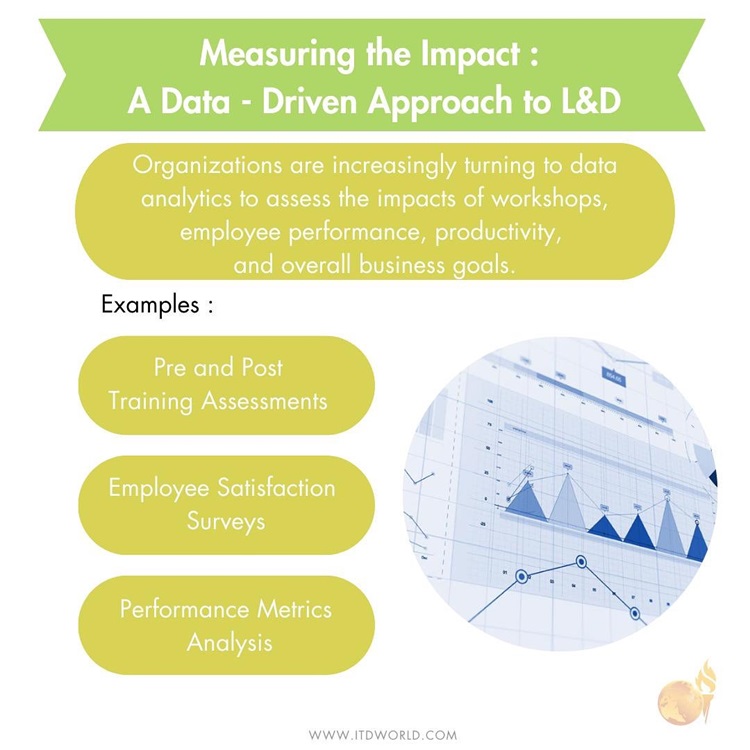
Measuring the Impact: A Data-Driven Approach to L&D
Organizations are increasingly turning to data analytics to assess the impact of training programs on employee performance, productivity, and overall business goals. This data-driven approach allows for a more strategic and accountable L&D function.
Examples:
- Pre- and Post-Training Assessments: Evaluating learner knowledge and skills before and after a training program helps assess knowledge gain and identify areas needing improvement.
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys: Gathering feedback from participants about the quality, relevance, and effectiveness of training programs allows for continuous improvement.
- Performance Metrics Analysis: Tracking changes in employee performance data, such as sales figures, customer satisfaction scores, or error rates, after training can demonstrate the impact on business outcomes.
How Organizations Can Prepare:
- Define Learning Objectives: Clearly define the specific goals and desired outcomes for each L&D program – as well as relevant metrics to track.
- Invest in Learning Analytics Tools: Utilize Learning Management Systems (LMS) and other analytics tools to track learner engagement, completion rates, and assessment scores.
- Develop a Measurement Strategy: Create a comprehensive plan for measuring the effectiveness of your L&D programs. This might involve identifying key metrics, defining data collection methods, and establishing tools for data analysis.
- Communicate the Value: Share the results of your L&D effectiveness measurements with stakeholders. This demonstrates the value of L&D to the organization and encourages continued investment in learning initiatives.
Read more: Employee Development Plan – Fueling Future Success
Learning and Development future trends
Final Thoughts
By incorporating these 10 L&D trends into your strategy, you can foster a culture of continuous learning, equip your employees with the in-demand skills for the future, and cultivate a thriving workforce that’s prepared to navigate the ever-changing landscape of work. As the future unfolds, these forward-thinking L&D approaches will be essential for organizations that aim to stay competitive and achieve long-term success.

Other resources you might be interested in:
- Talent Transformation: Build a Future-ready Workforce
- HR Transformation: A Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Future-Proof Workforce
- Talent Management: Mastering the Basics for Success
- Talent Development Playbook: Building Your Future Workforce
- Organization Development (OD): A Closer Look

