Metadata is often described as “data about data,” but its role in CRM data migration extends far beyond that.
Metadata provides essential context and structure, facilitating the accurate transfer of data while maintaining its integrity and relationships.
Whether you are transitioning to a new platform or upgrading your CRM system, managing metadata effectively ensures a seamless and efficient migration process.
Understanding Metadata in CRM
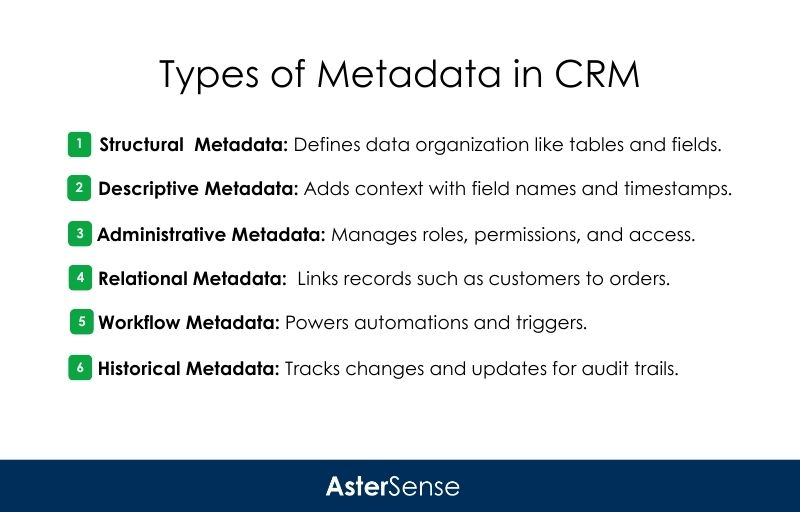
In the context of CRM systems, metadata provides descriptive information that offers context to the actual data stored within the CRM.
This includes details such as field names, data types, relationships between data entities, and user permissions.
Essentially, metadata defines the structure and organization of your CRM data, ensuring that each piece of information is accurately categorized and interconnected.
Why Metadata is Critical in CRM Data Migration?
Metadata isn’t just supplementary information; it is the backbone that ensures your CRM data migration is accurate and effective. Here’s why metadata is indispensable:
1. Preserving Data Relationships
CRM systems store relational data, such as linking deals to contacts or accounts. Metadata ensures these relationships are maintained during migration.
Example: When migrating to Pipedrive services, metadata ensures that a deal stays connected to its corresponding organization and contact records.
2. Maintaining Data Integrity
Without metadata, inconsistencies like mismatched data types or missing fields can arise.
For instance, if a source system has a numeric field, but the target CRM expects text, the migration could fail or produce errors.
3. Migrating Custom Configurations
Modern CRMs support extensive customizations, such as custom fields, workflows, and options. Metadata ensures these configurations are accurately migrated, allowing the new CRM to function just as effectively.
Example: Custom pipeline stages or dropdown options in Pipedrive can be recreated using metadata.
4. Enhancing Usability and Automation
Metadata-driven migrations allow APIs and integrations to work seamlessly in the target CRM, as metadata informs them about the structure of data entities and attributes.
Effective Steps to Utilize Metadata in Migration
To harness the full potential of metadata during CRM migration, follow these strategic steps:
1. Conduct a Metadata Audit
Start by thoroughly reviewing the metadata in your current CRM. This includes assessing field properties, customizations, and dependencies. Identify and address any inconsistencies or outdated metadata that could impede the migration.
2. Develop a Metadata Mapping Plan
Create a comprehensive mapping plan that aligns fields, relationships, and workflows between the source and target CRMs. Utilizing metadata templates or specialized tools to document these mappings ensures clarity and consistency throughout the migration process.
3. Utilize Metadata Extraction Tools
Leverage tools such as Salesforce Metadata API, HubSpot Operations Hub, or other third-party solutions to extract and analyze metadata from your source CRM. By validating its structure and content, ensure the extracted metadata is compatible with your target CRM.
4. Perform Test Migrations
Execute test migrations to verify that metadata transfers accurately, including field relationships and custom configurations. Address any issues identified during these tests to prevent complications during the complete migration.
5. Optimize and Update Metadata Post-Migration
After completing the migration, review the metadata in your new CRM to identify opportunities for optimization. Update metadata to reflect changes in business processes or requirements, ensuring continued efficiency and relevance.
Examples of Metadata in CRM Data Migration
Let’s look at some examples using Pipedrive CRM to show how metadata works in CRM migration. These examples explain how metadata helps move your data smoothly and keeps everything organized.
1. Entity Metadata
Example: Migrating Contacts
Entities are the main components of a CRM, such as deals, contacts, and organizations. Metadata defines the structure of these entities, including the fields they contain and their relationships.
How It Works: When migrating contacts to Pipedrive, metadata ensures each contact retains essential information like name, email, and phone number. It also maintains links to related Deals and Organizations using unique identifiers (deal_id and org_id).
Technically, this involves mapping the source CRM’s fields to Pipedrive’s API endpoints (GET /persons and POST /persons), ensuring data consistency and integrity.
2. Field Metadata
Example: Migrating a Custom Field
Custom fields capture specific information unique to your business, such as “Preferred Contact Method. Metadata describes these fields, including their type (e.g., text or dropdown) and allowed values.
How It Works: If your old CRM has a dropdown field for “Preferred Contact Method” with options like Email, Phone, or In-Person, metadata ensures these options are accurately recreated in Pipedrive.
This is done by defining the field type (enum) and mapping the values using Pipedrive’s POST /personFields API. Tools like Talend can automate this mapping, ensuring customer preferences are preserved correctly.
3. Relationship Metadata
Example: Linking Deals and Contacts
Relationships show how different entities interact within the CRM. Metadata captures these connections to maintain data integrity during migration.
How It Works: When migrating Deals, metadata ensures each Deal is linked to the correct Contact and Organization. This involves preserving unique identifiers (deal_id, person_id, org_id) and using Pipedrive’s batch API requests to transfer and link records efficiently. Validation checks are performed to ensure all linked entities exist in Pipedrive, preventing broken relationships.
4. Permissions and User Roles
Example: Migrating User Permissions
Permissions and roles determine who can access or modify different parts of the CRM. Metadata outlines these permissions to ensure they are correctly applied in the new CRM.
How It Works: User roles like Administrator, Manager, or User are defined in Pipedrive using its role management API. Metadata migration involves mapping the source CRM’s roles to Pipedrive’s roles and assigning access scopes (e.g., Deals, Contacts).
Automated scripts can handle this mapping, ensuring each user retains the appropriate permissions and access levels and maintains security and proper data access.
Common Challenges with Metadata in CRM Migration
While metadata is indispensable, migrating it can present several challenges:
1. Inconsistent Metadata Across Systems
Variations in metadata structures between the source and target CRMs can complicate mapping, requiring careful planning and possibly custom solutions.
2. Missing or Incomplete Metadata
Incomplete metadata in the source CRM can lead to broken relationships or misaligned fields, necessitating thorough audits and data cleaning before migration.
3. Outdated Metadata
Legacy systems may contain obsolete metadata that requires updating to align with modern CRM standards and functionalities.
4. Custom Metadata Handling
Migrating highly customized metadata, such as unique fields and workflows, can be complex and may require specialized tools or expertise to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Metadata migration is the backbone of a successful customer relationship management (CRM) data migration. It preserves the structure, relationships, and usability of data, ensuring a smooth transition to systems like Pipedrive CRM.
Need help with metadata-driven CRM migration? Contact Astersense today for tailored solutions to ensure your data and workflows remain intact!
Note: The content on this article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. ITD World is not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided here.